Surrounded Regions
题目描述
Given a 2D board containing'X'and'O', capture all regions surrounded by'X'.A region is captured by flipping all'O's into'X's in that surrounded region .
For example,
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X X
After running your function, the board should be:
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X O X X
解题思路
这道题的意思是,将边界及所有与边界相连的O予以保留,其它的O变为X。
所以我们可以采取的思路是,将边界及所有与边界相连的O先行转换成别的字母,例如S。然后遍历整个矩阵,将所有的O变为X,所有的S变为O,这样就完成了任务。
代码实现
void toS(vector<vector<char>> &board, int i, int j,int rows, int cols)
{
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= rows || j >= cols)
return;
if (board[i][j] == 'O')
{
board[i][j] = 'S';
toS(board, i + 1, j, rows, cols);
toS(board, i - 1, j, rows, cols);
toS(board, i, j - 1, rows, cols);
toS(board, i, j + 1, rows, cols);
}
}
void solve(vector<vector<char>> &board) {
int rows = board.size();//行数
int cols = board[0].size();//列数
if (rows <= 2 || cols <= 2)
return;
//第一行
for (int i = 0; i < cols; i++)
{
if (board[0][i] == 'O')
toS(board, 0, i,rows,cols);
}
//最后一行
for (int i = 0; i < cols; i++)
{
if (board[rows - 1][i] == 'O')
toS(board, rows - 1, i, rows, cols);
}
//第一列
for (int i = 1; i < rows - 1; i++) {
if (board[i][0] == 'O')
toS(board, i, 0, rows, cols);
}
//最后一列
for (int i = 1; i < rows - 1; i++)
{
if (board[i][cols - 1]=='O')
toS(board, i, cols - 1, rows, cols);
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
if (board[i][j] == 'O')
board[i][j] = 'X';
else if (board[i][j] == 'S')
board[i][j] = 'O';
}
}
}
Valid-Parentheses
题目描述
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
1. 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
2. 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
3. 注意空字符串可被认为是有效字符串。
示例 1:
输入: "()"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: "()[]{}"
输出: true
示例 3:
输入: "(]"
输出: false
示例 4:
输入: "([)]"
输出: false
示例 5:
输入: "{[]}"
输出: true
题目解析
这种匹配问题,我们有这种思想,可以用栈来解决这个问题。因为合法的匹配实际上是类似于{[()]}这样的匹配,你会发现先输入的符号相匹配的右半边是最后输入,也就是说符合栈先入后出的特性。当pop完了这个栈为空,那就说明匹配。所以我们可以设计这这样一个算法:遍历整个字符串的每一个字符,然后:
1. 如果字符是左侧符号(如{``(``[)那么我们就向堆栈里面push进去;
2. 当字符不是左侧符号的时候,首先要判断堆栈此时是否为空,若为空返回false,因为左侧符号还未匹配完;如果栈不为空,判断此时栈顶元素是否与当前元素相等,若不相等,也返回flase;若相等,pop出来,继续走下去。
3.当所有字符遍历完,这个时候判断栈是否为空,若为空说明都匹配,返回true,否则返回false。
代码实现
bool isValid(string s) {
int slen = s.size();
if (slen == 0)
return true;
if (slen < 2)
return false;
stack<char>cstack;
for (int i = 0; i < slen; i++)
{
if (s[i] == '(')
cstack.push(')');
else if (s[i] == '[')
cstack.push(']');
else if (s[i] == '{')
cstack.push('}');
else if (cstack.empty() || cstack.top() != s[i])
return false;
else
cstack.pop();
}
return cstack.empty();
}
remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list
题目描述
Given a linked list, remove the n th node from the end of list and return its head.
Given linked list: 1->2->3->4->5, and n = 2.
After removing the second node from the end, the linked list becomes 1->2->3->5.
Note: Given n will always be valid.Try to do this in one pass.
解题思路
要求只能走一次路径,所以启发我们使用快慢指针。由于给予n总是合法的,所以我们不需要判断n是否超过链表长度(如果需要判断的话,必然不可能只走一趟)。
假设我们的链表是1->2->3->4->5,且n=2。那么我们初始状态下,链表如下:
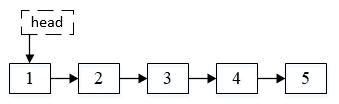
第一步,首先建立一个头指针,命名为dummy,算是一个pivot,然后令head也指向这个dummy。
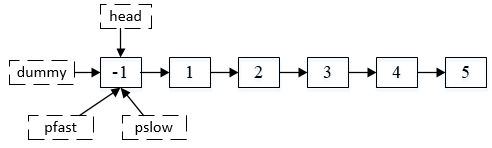
第二步,新建快指针pfast、慢指针pslow,然后分别指向dummy。
到目前为止,链表关系如下图所示:
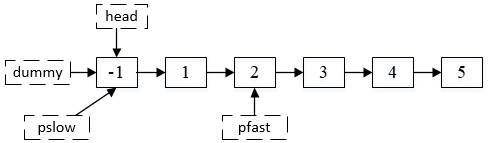
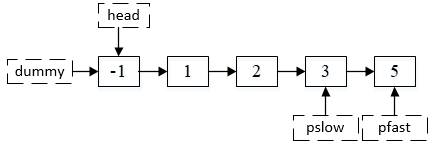
第三步,这一步很关键。就是后移pfast指针n个位置,在这里就是2个位置。结果如下:
第四步,在完成上述操作之后,开始同时移动pfast和pslow,直到pfast的next指针为空的时候停止移动。这个时候的结果如下:
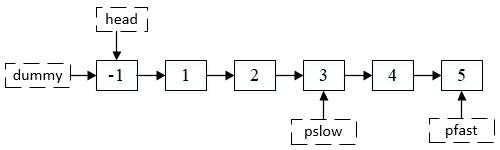
第五步,我们新建一个链表指针指向pslow的next,命名为delp节点,这就是我们待删除的位置。然后令pslow的next指向5的地址(pslow->next=pslow->next->next)。
第六步,删除delp节点,也就是执行delete(delp)命令。
最后,返回dummy->next即可。结果如下:
代码实现
ListNode *removeNthFromEnd(ListNode *head, int n) {
if (head == NULL)
return head;
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
head = dummy;
ListNode *pslow = head;
ListNode *pfast = head;
while (n--)
{
pfast = pfast->next;
}
while (pfast->next != NULL)
{
pslow = pslow->next;
pfast = pfast->next;
}
ListNode *delp = pslow->next;
pslow->next = pslow->next->next;
delete delp;
return dummy->next;
}


文章评论