Leetcode 1:两数之和
题目描述
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,你不能重复利用这个数组中同样的元素。
示例
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
题目解析
直接看代码即可,非常清晰
代码实现
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<int>res(2,-1);
map<int,int> tmp;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(tmp.count(target-nums[i]))
{
res[0]=tmp[target - nums[i]];
res[1]=i;
break;
}
tmp[nums[i]]=i;
}
return res;
}
复杂度
Leetcode 19:删除链表的倒数第N个节点
题目描述
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2.
当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 1->2->3->5.
代码实现
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
if (head == NULL )
return head;
ListNode *dummy=new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *pre = dummy;
ListNode *end = dummy;
//Move end to n+1
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
end = end->next;
}
while (end != NULL)
{
pre = pre->next;
end = end->next;
}
ListNode *dpoint = pre->next;//待删除的点
pre->next = dpoint->next;
delete(dpoint);
return dummy->next;
}
复杂度
时间复杂度O(n)
Leetcode 70:爬楼梯
题目描述
题目解析
我们很容易就发现,由于我们可以走一步也可以走两步,那实际对于第n个台阶来说,其依赖于走第n-1阶有多少种方法(此时只需要再走1步即可)和走第n-2阶有多少种方法(此时只需要再走2步即可),也就是说f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2),为一个斐波那契数列。递归形式很简单,所以这里写了一个迭代形式。
代码实现
int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
if (n == 2)
return 2;
int first = 1, second = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
{
int third = first + second;
first = second;
second = third;
}
return second;
}
复杂度
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度O(1)。
Leetcode 78:子集
题目描述
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例
输入: nums = [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[3],
[1],
[2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[]
]
代码实现
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> temp;
vector<vector<int>> r;
dfs(r, temp, nums, 0);
return r;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& r, vector<int>& temp, const vector<int>& nums, int begin)
{
r.push_back(temp);
for (int i = begin; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
temp.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(r, temp, nums, i + 1);
temp.pop_back();
}
}
实现消耗
Leetcode 79:单词搜索
题目描述
给定一个二维网格和一个单词,找出该单词是否存在于网格中。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例
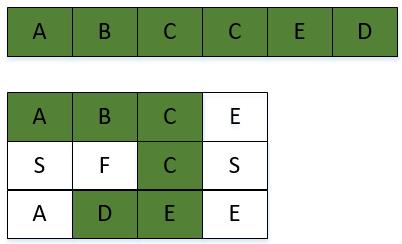
board =
[
['A','B','C','E'],
['S','F','C','S'],
['A','D','E','E']
]
给定 word = "ABCCED", 返回 true.
给定 word = "SEE", 返回 true.
给定 word = "ABCB", 返回 false.
解题思路
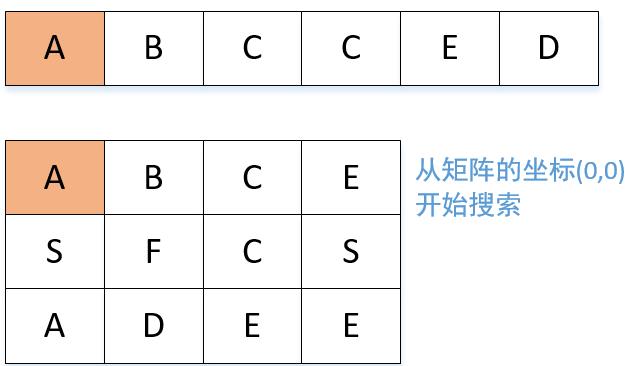
看这个题,我们自己脑子里先有一个思路:首先遍历这个矩阵,寻找到第一个对应的字母,然后再对其上下左右方向进行搜索,寻找下一个字母。
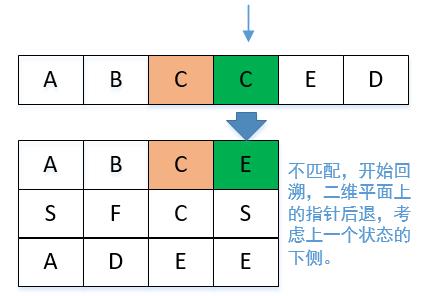
我们还需要注意可能存在这样一种情况,比如说在矩阵中有两个A,其中第一个A的上下左右不符合我们的要求,而第二个A则符合。此时当我们遍历到第一个A的时候,符合要求,开始对它的上下左右搜索,结果搜索不到,此时不应该单纯返回false然后判断找不到,而是应该继续遍历这个矩阵,寻找第二个A。
所以这个题可以使用回溯法解决,涉及到了深度优先遍历和状态重置。
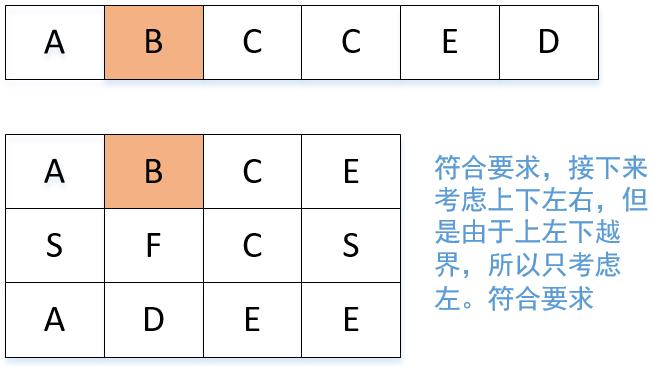
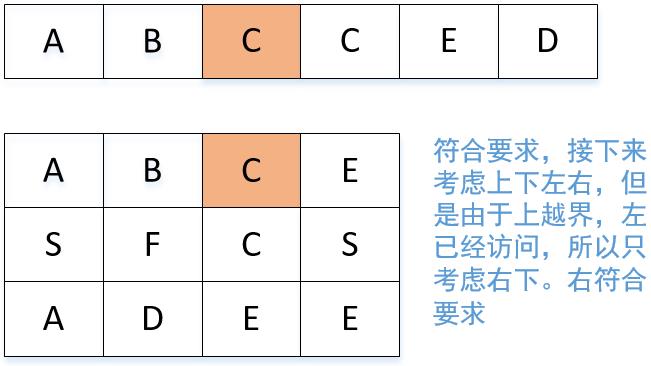
我们结合ABCCED这个组合来顺一遍代码。
代码实现
vector<vector<int>>dir{ {-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1} };
bool edfs(int x, int y, int ind, vector<vector<char>>& board, string& word, vector<vector<bool>>& visited)
{
//word长度为1的情况
if (ind == word.size() - 1)
return word[ind] == board[x][y];
//其它情况
if (word[ind] == board[x][y])
{
visited[x][y] = true;//找到了,在visited中相应坐标标记
//然后开始在上下左右寻找下一个字母
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int new_x = x + dir[i][0];
int new_y = y + dir[i][1];
if (new_x >= 0 && new_x < board.size() && new_y >= 0 && new_y < board[0].size() && !visited[new_x][new_y])
{
if (edfs(new_x, new_y, ind + 1, board, word, visited))
return true;
}
}
visited[x][y] = false;
}
//字符找不到
return false;
}
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
int row = board.size();
int col = board[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited(row, vector<bool>(col));
//从矩阵的第一个元素开始寻找与word第一个字母相对应的字母,若找不到,则j+1,j加到最后,就i+1,这样一行一行查找。
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if (edfs(i, j, 0, board, word, visited))
return true;
}
}
//找不到就返回false
return false;
}
复杂度


文章评论