valid sudoku
题目描述
Determine if a Sudoku is valid, according to: Sudoku Puzzles - The Rules.The Sudoku board could be partially filled, where empty cells are filled with the character'.'.
题目解析
数独具有以下规则:
- 每一行所有元素不能重复(1~9);
- 每一列所有元素不能重复(1~9);
- 由第3i~3(i)+2行和第3i~3(i)+2列组成的九宫格内元素不能重复(其中0<=i<n/3-1,元素仍为1~9)。
想到重复问题,自然而然我们想到了设置Flag的方法,由此我们可以设置3个n×n大小的矩阵来作为标志位:
- 第一个矩阵命名为fRow,作为判断每一行的数字是否重复的矩阵,因为元素只能为1~9,所以正好每行9个格子合适。
- 第二个矩阵命名为fCol,作为判断每一行列的数字是否重复的矩阵,因为元素只能为1~9,所以正好每行9个格子合适。
- 第三个矩阵命名为fMat,作为判断每个九宫格的数字是否重复的矩阵。
本题的特殊之处在于允许有空格的格子,且空格的地方以字符.表示,且所存储的数字都是char类型,因此首先要进行一个类型转换才能判断:
if(board[i][j] >= '1' && board[i][j]<='9')
int temp = board[i][j]-'1';
若检测到该行出现这个数字,则设置该行这个位置为true,当又遍历到这个数字的时候,若检查发现这个位置已经设置为true了,则返回false。当然在实现代码的时候,要把判断放在前面,把设置标志位放在后面。
该方法的时间复杂度为O(n2),空间复杂度为O(n2)。
代码实现
bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char> > &board) {
int totalRows = board.size();
int totalCols = board[0].size();
if(totalRows == 0 || totalCols == 0)
return false;
vector<vector<bool> > fRow(totalRows,vector<bool>(totalCols,false));//行标志矩阵
vector<vector<bool> > fCol(totalRows,vector<bool>(totalCols,false));//列标志矩阵
vector<vector<bool> > fMat(totalRows, vector<bool>(totalCols,false));//9宫格标志矩阵
for(int i = 0;i < totalRows; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < totalCols; j++)
{
if(board[i][j] >= '1' && board[i][j]<='9')
{
int temp = board[i][j]-'1';
if(fRow[i][temp] || fCol[temp][j] || fMat[3*(i/3)+j/3][temp])
return false;
fRow[i][temp] = true;
fCol[temp][j] = true;
fMat[3*(i/3)+j/3][temp] = true;
}
}
}
return true;
}
largest rectangle in histogram
题目描述
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.
For example,Given height =[2,1,5,6,2,3],return10.
题目解析
我们以[2,1,5,6,2,3]为例来思考这个题目的思想。观察如图所示。
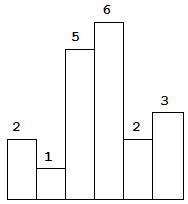
代码实现
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height) {
int maxarea = 0;
stack<int>stk;
for (int i = 0; i < height.size(); i++)
{
//如果堆栈是空的或者堆栈里面的最大数小于当前数组的元素,则当前数组元素入栈
if (stk.empty() || stk.top() <= height[i])
stk.push(height[i]);
else {
//如果堆栈非空且栈顶元素大于当前元素的话
int count = 0;
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top() > height[i])
{
count++;
maxarea = max(maxarea, stk.top()*count);
stk.pop();
}
while (count--)
stk.push(height[i]);
stk.push(height[i]);
}
}
int count = 1;
while (!stk.empty())
{
maxarea = max(maxarea, stk.top()*count);
stk.pop();
count++;
}
return maxarea;
}
pascals-triangle-ii
题目描述
Given an index k, return the k th row of the Pascal's triangle.For example, given k = 3,
Return[1,3,3,1].
题目解析
代码实现
vector<int> getRow(int rowIndex) {
vector<vector<int> > tempresult(rowIndex+1);//传回的二维数组
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i <= rowIndex; ++i)
{
tempresult[i].push_back(1);
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
tempresult[i].push_back(tempresult[i - 1][j - 1] + tempresult[i - 1][j]);
if (i > 0)
tempresult[i].push_back(1);
}
return tempresult[rowIndex];
}
Construct binary tree from preorder and inorder traversal
题目描述
Given preorder and inorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree.
Note:
You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the tree.
思路
关于根据前序和中序如何得到二叉树的结构的计算方式,我就不重复了,之前的程序里面也有,这里就只说说代码里几个参数的思路。
**一定要做边界条件的判断!***
root->left = build(preorder, pstart + 1, pstart + i - istart, inorder, istart, i - 1);
root->right = build(preorder, pstart + i - istart + 1, pend, inorder, i + 1, iend);
对于左子树处理来说,中序遍历所要处理的位置就是根节点左侧的所有数字,所以自然起始位置就是istart,结束位置就是i-1;对于前序遍历来说表示就麻烦一些,起始位置还好,是pstart+1,结束位置是pstart+(i-istart),其中i-istart是左子树的元素数。
对于右子树处理来说,中序遍历所要处理的位置就是根节点右侧的所有数字,所以自然起始位置就是i+1,结束位置就是iend;对于前序遍历来说,就是从左侧子树最后一个元素后面那个数字到最后一个,所以起始位置是pstart + i - istart + 1,结束位置是pend。
代码实现
TreeNode *buildTree(vector<int> &preorder, vector<int> &inorder) {
int presize = preorder.size();
int insize = inorder.size();
if (presize == 0 || insize == 0)
{
return NULL;
}
else if (presize != insize)
return NULL;
return build(preorder, 0, presize - 1, inorder, 0, insize - 1);
}
TreeNode* build(vector<int>&preorder, int pstart, int pend, vector<int>&inorder, int istart, int iend)
{
if (pstart > pend || istart > iend)
return NULL;
int mid = preorder[pstart];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(mid);
int i = istart;
for (; i <= iend; ++i)
{
if (inorder[i] == mid)
break;
}
root->left = build(preorder, pstart + 1, pstart + i - istart, inorder, istart, i - 1);
root->right = build(preorder, pstart + i - istart + 1, pend, inorder, i + 1, iend);
return root;
}


文章评论