unique path
题目描述
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below).The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below).How many possible unique paths are there?
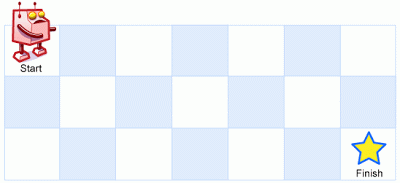
Above is a 3 x 7 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?Note: m and n will be at most 100.
题目解析
自己就是想不出来动态规划里面的问题如何来划分为合适的子问题(也就是写不出递推公式)。每次都是看了答案恍然大悟。其实这个题的递推公式非常之简单。就是:
当前点的路径=上面一个点的路径+左边一个点的路径。
也就是
path[i][j]=path[i-1][j]+path[i][j-1];
代码实现
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
vector<vector<int> >path(m,vector<int >(n,1));
for(int i=1;i<m;i++)
for(int j=1;j<n;j++)
{
path[i][j]=path[i-1][j]+path[i][j-1];
}
return path[m-1][n-1];
}
n queens ii
题目描述
Follow up for N-Queens problem.Now, instead outputting board configurations, return the total number of distinct solutions.
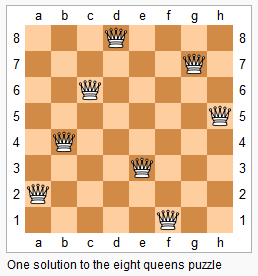
题目解析
我们令x[i]的值为第i个皇后所在的列数。那么我们第一个皇后的位置可以在第一行任意一个位置任选,所以我们试出来第一个皇后在第1到第n个列位置下的不同情况(一共有n颗n叉树)。然后安排完第一个皇后位置后,第二个皇后位置在第二行也是从第1到第n列分别试一遍,看是否满足要求。若满足要求则进行第三个皇后,否则该树是没有结果的。当不断递归到t>n的时候,那说明在上一步已经安排完了,那么久直接对计数加1,然后返回。
void Backtrack(int t,int num)
{
if(t>num)
{
countn++;
}
else
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++)
{
x[t]=i;
if(Place(t))
Backtrack(t+1,num);
}
}void Backtrack(int t,int num)
{
if(t>num)
{
countn++;
}
else
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++)
{
x[t]=i;
if(Place(t))
Backtrack(t+1,num);
}
}
题目要求就是每一个皇后不能跟上一行的那个皇后同一列和对角线,所以在获得下一列真实的位置的时候,需要判断是不是在同一列或者对角线,即:
bool Place(int t)
{
bool ok=true;
for(int j=1;j<t;j++)
{
if(x[t]==x[j]||t-j==fabs(x[t]-x[j]))//判断列对角线是否冲突
{
ok=false;
break;
}
}
return ok;
}
代码实现
public:
int countn=0;
int x[200];
bool Place(int t)
{
bool ok=true;
for(int j=1;j<t;j++)
{
if(x[t]==x[j]||t-j==fabs(x[t]-x[j]))//判断列对角线是否冲突
{
ok=false;
break;
}
}
return ok;
}
void Backtrack(int t,int num)
{
if(t>num)
{
countn++;
}
else
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++)
{
x[t]=i;
if(Place(t))
Backtrack(t+1,num);
}
}
int totalNQueens(int n) {
Backtrack(1,n);
return countn;
}
merge sorted array
题目描述
Given two sorted integer arrays A and B, merge B into A as one sorted array.Note:
You may assume that A has enough space to hold additional elements from B. The number of elements initialized in A and B are mand n respectively.
题目解析
由于数组A的空间足够,为了不使用额外空间,我们很容易想到从后往前进行。该题目分为两步完成。
第一步:从后往前进行插入,也就是说比较的时候从A和B已有元素的最后一个元素开始比较,大的插入到A的未插入的最后一个位置。
完成上述操作的前提是,A和B的待排元素都还有,所以判断条件就是下面的
x1>=0 && x2>=0
对于上述操作的实现如下:
A[index--] = A[x1] > B[x2] ? A[x1--] : B[x2--];
这句话其实就是下面这段话的意思:
if(A[x1]>B[x2])
{
A[index]=A[x1];
--index;
--x1;
}
else
{
A[index]=B[x2];
--index;
--x2;
}
第二步:在第一步完成情况下存在两种情况:
- 原来的A和B都已经完整插入到A中,即x1=-1且x2=-1。
- 原来B已经插入完毕了但是A还没有,即x2=-1且x1>=0,此时A剩下的数字都在正确的位置,不需要再排序了。
- 原来的A插入完毕了,B还没有,即x1=-1且x2>=0,那就直接把B插入到剩下的位置即可。
代码实现
void merge(int A[], int m, int B[], int n) {
int total = m + n;
int x1 = m - 1;
int x2 = n - 1;
int index = total - 1;
while (x1 >= 0 && x2 >= 0)
{
A[index--] = A[x1] > B[x2] ? A[x1--] : B[x2--];
}
while (x2 >= 0)
A[index--] = B[x2--];
}


文章评论